Long chain fatty acid: Palmitoleic acid (9-cis-hexadecanoic acid or cis-palmitoleic acid)
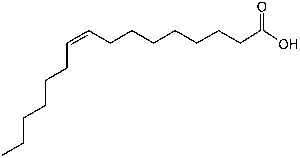 This is palmitoleic acid or 9-cis-hexadecanoic acid. What can we ascertain about this fatty acid?
This is palmitoleic acid or 9-cis-hexadecanoic acid. What can we ascertain about this fatty acid?
It has a double bond, so it’s unsaturated.
It has one double bond, so it’s monounsaturated.
The double bond looks like a cis double bond – the molecule is flat where where the double bond is located, which usually means it’s cis. (We can see from the name that it’s cis.)
It has 16 carbon atoms with one double bond, so it’s C16:1, cis-9 with a molecular formula of C16H30O2

This fatty acid is famously found in a good quantities in two of our liquid oils – macadamia nut oil at 18% to 22% and sea buckthorn oil at up to 36.3% – and in some other ones, like emu oil at 3.5%, jojoba oil at 2%, moringa oil at up to 5%, tamanu oilat up to 5%, and sweet almond oil at 2%.
Palmitoleic acid is a building block in our skin to prevent burns, wounds, and skin scratches, and is an active anti-microbial. Nice! Sounds like something we could use in so many of our products!
Because it has that kink, as we learned in part 19 of my introduction to chemistry series, we can guess the melting point will be lower than palmitic acid (C16:0) because the molecules won’t pack together well thanks to the cis double bond.
The melting point is -0.1˚C (32˚F). Holy cow! That’s such a difference! This means this fatty acid is liquid at room and body temperature. Heck, it’s even liquid in the fridge!
