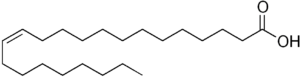
 Erucic acid (C22:1, ω9) is a monounsaturated fatty acid – aka cis-13-docosenoic acid – is a considered a fatty acid that contributes to “drying” oils, or those that can polymerize when exposed to air.
Erucic acid (C22:1, ω9) is a monounsaturated fatty acid – aka cis-13-docosenoic acid – is a considered a fatty acid that contributes to “drying” oils, or those that can polymerize when exposed to air.
These fatty acids form into triglycerides that are considered “drying”, that is to say they will “harden to a tough, solid film after a period of exposure to air, the oil hardens through a chemical reaction in which the components cross-link (…polymerize)…as a result of auto-oxidation. The adding of oxygen to an organic compound…” (Reference)
The film is a uniform, plasticized*, soft-solid film that can protect hair and skin, but remains flexible. This is how it works as an anti-frizzing ingredient – it prevents water from entering the hair cuticle – and a shine enhancer – light bounces off the uniform film on the hair strand. It works on our skin to prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and protects skin from the elements, like wind, snow, cold, and so on. This is a really unique process limited to oils, like mongongo (manketti) oil and other “drying” oils.
It’s found in broccoli seed oil.
It’s considered a very long chain fatty acid – one that has more than 22 carbon atoms in the chain.
The melting point is 33.8˚C, so it’s solid at room temperature. Any liquid oil that contains this fatty acid will be thicker at room temperature because this fatty acid is solid. The molecular weight is 338.576 grams per mol.
