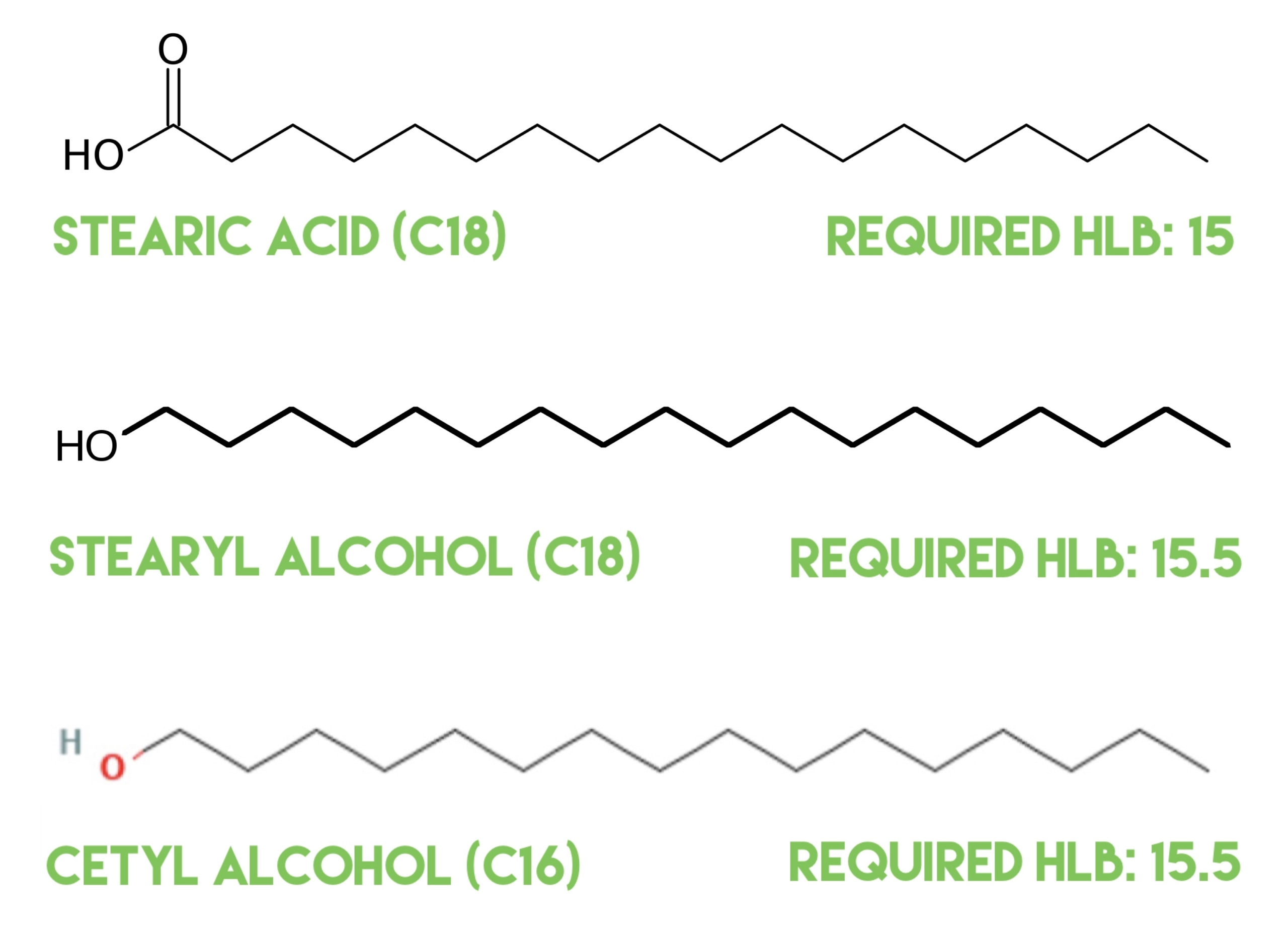
Cetyl alcohol, cetearyl alcohol, and stearic acid are not emulsifiers! Let’s demonstrate this by looking at molecules and the HLB system
I’ve been asked quite a few times in over the last year or two if Cetyl Alcohol, Cetearyl Alcohol, and stearic acid are emulsifiers, and the answer is no, they’re structuring agents, oil soluble ingredients that have a required HLB. They are not emulsifiers. They aren’t surfactants. They can’t bring oil and water together to...