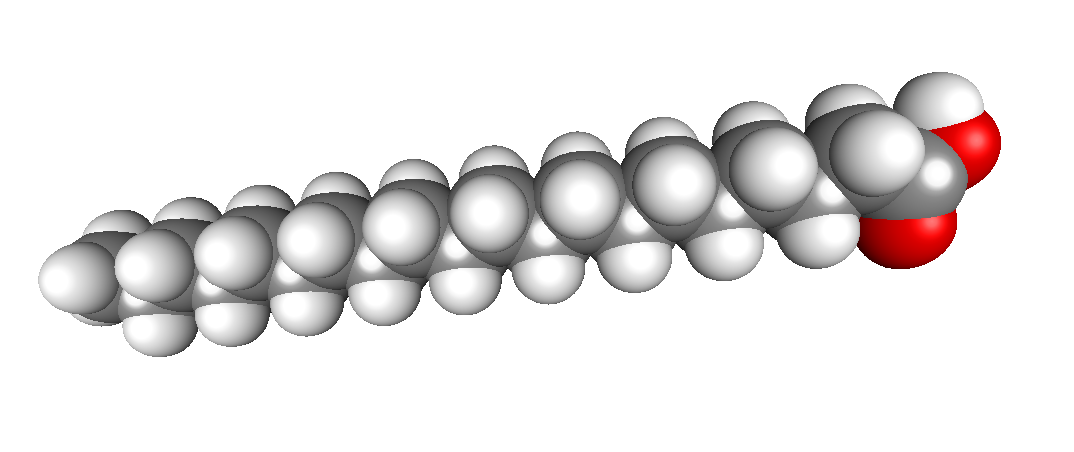
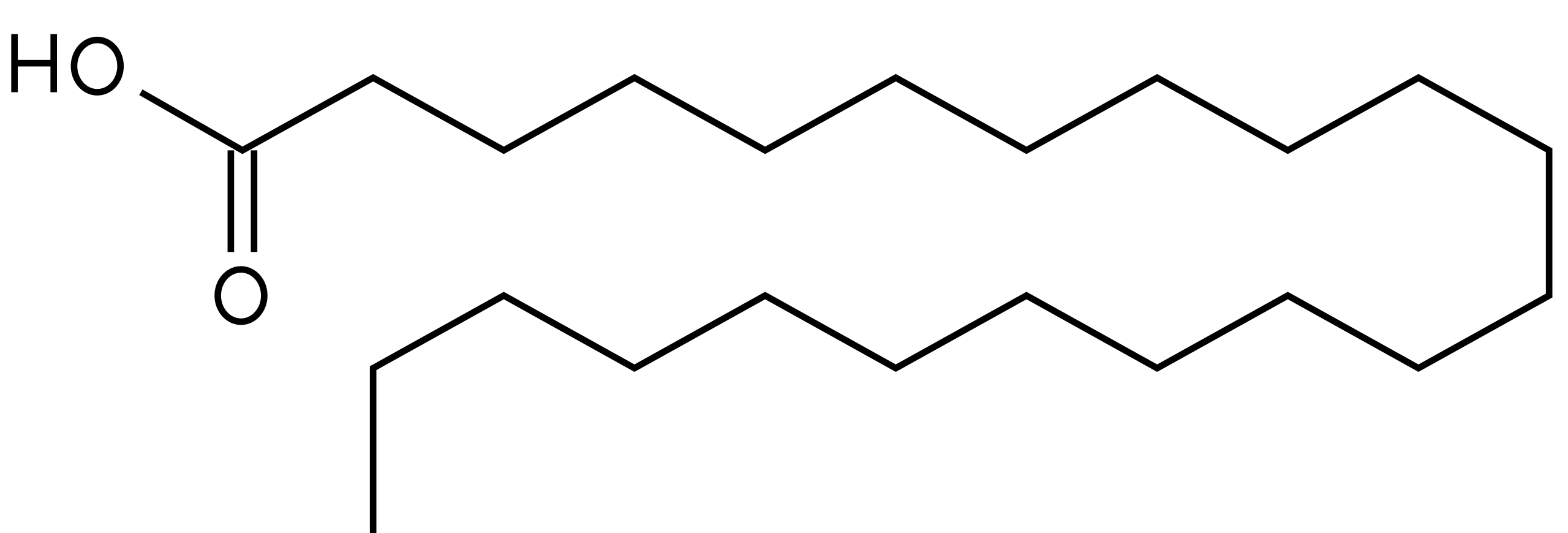
#alltheingredients: Arachidic fatty acid (eicosenoic acid)
Arachidic fatty acid is a saturated, straight chain fatty acid with 20 carbon atoms in the chain. It has a melting point of 75˚C (167˚F), and a boiling point of 328˚C, so it can handle being heated and held. It’s found in a number of our favourite oils and butters – cupuacu butter, illipe butter,...